Have you been diagnosed with osteoarthritis in the knee joint, are you in severe pain and starting to limp?Are you looking for a place to get treatment?Contact a medical center that will help you relieve pain, find out the causes of the disease and provide the necessary treatment.We have more than 20 effective joint rehabilitation methods in our arsenal.
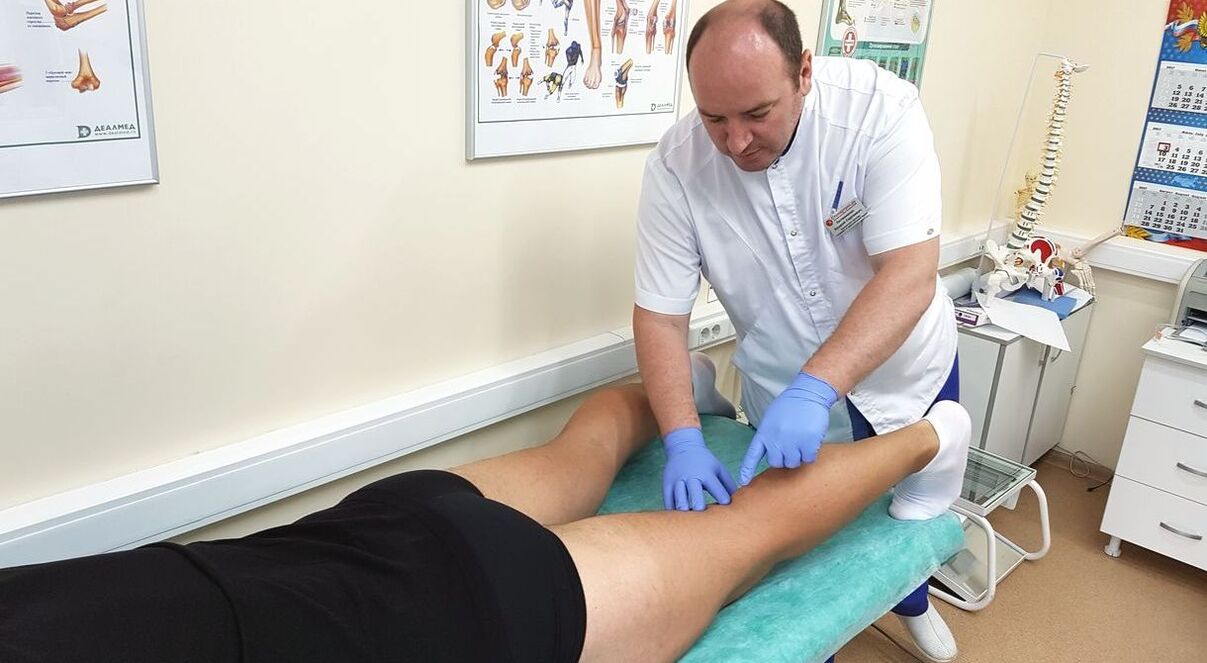
The disease is also known as gonarthrosis (from Latin genu - knee), osteoarthrosis (as the disease was previously called) and osteoarthritis (the term reflects the mechanism of development and modern understanding of the disease).Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint is chronic and develops over several years.The majority of patients are over 50 years old.Women predominate in 2/3 of cases.
How does the disease develop?
Under the influence of external and internal factors, the blood supply and nutrition of the tissue is disrupted, degenerative-dystrophic damage to the articular cartilage occurs, with the subsequent involvement of the underlying bone in the inflammatory process.Destruction of the articular surfaces leads to loss of joint function, restricts movement and impairs the patient's quality of life.
Causes and risk factors
The main reasons for the development of osteoarthritis:
- Hard physical work.Constant loads on the legs lead to microtrauma of the cartilage and the development of the inflammatory process.Loaders, plumbers, miners and quarry workers are at risk.Deforming osteoarthritis often affects professional athletes (weightlifters, cyclists, tennis players, soccer players, basketball players, hockey players, etc.).
- Injuries.Damage to ligaments, tendons, menisci, bruises and fractures lead to disruptions in the biomechanics of the joint.If treated incorrectly, this leads to the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
- Surgical interventions on the knee can lead to the development of pathology of the articular cartilage and surrounding tissues.
- Excess weight increases the load on the joints of the lower extremities.Up to 80-90% of the progression of all osteoarthritis is associated with joint overload.
- Age.In people over 50-60 years old, regeneration processes slow down, collagen production decreases, and hormone levels suffer.Which leads to the development of pathology.
- Hormonal changes in women.During menopause, the production of estrogen decreases, which disrupts the absorption of calcium, leads to a weakening of the musculoskeletal system and makes bones brittle.The risk of developing osteoporosis increases.
- Thyroid problems.Thyroid hormones are involved in the metabolic processes of calcium and phosphorus in the body.Their deficiency or excess can cause knee osteoarthritis.
- Genetic predisposition.Collagen mutation can lead to disruption of connective tissue elements, leading to a deterioration in the shock-absorbing function of articular cartilage.
- Inheritance.There is a high probability of developing the disease if there are relatives in the patient's family with a diagnosis of gonarthrosis, mainly in the female line.
- Inflammatory diseases.Infectious arthritis, bursitis and synovitis caused by bacterial or viral infection are often complicated by the development of gonarthrosis.
- Vascular diseases.The tissue is not properly nourished, the blood supply is impaired, which leads to the development of ischemia and degenerative-dystrophic changes in the articular cartilage.
- Poor nutrition and metabolic disorders.Eating foods high in purines (proteins) contributes to the deposition of salts in the knee, for example in gouty arthritis.
- Certain diseases such as gonorrhea, tuberculosis, syphilis, chlamydia and influenza can cause serious joint damage.
- Poisoning of the body with various chemicals, including some medications.
- Autoimmune diseases are associated with a violation of the body's immune defenses when antibodies are formed against its own cells, for example in rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of gonarthrosis:
- Pain in the joint, aching in nature, sometimes at night, in case of exacerbation, severe stitching;
- Crunching and clicking during movement are caused by a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces, the presence of osteophytes and cartilage defects;
- Swelling and swelling are associated with the development of an inflammatory process in the joint and surrounding soft tissues;
- Deformation of the joint space and limb axis indicates disease progression;
- Atrophy and weakness of the thigh muscles, the volume of the quadriceps and biceps muscles decreases;
- The limitation of mobility and stiffness in the joint is caused by pain, the development of adhesions and the appearance of osteophytes (bone spines).
The first sign of osteoarthritis to look out for is pain that occurs during or after exercise.The pain disappears at rest and does not require medication.Morning stiffness in the knee, beginning pain, before getting up and walking after sleeping, it takes some time for the joint to develop.
Signs of deterioration
As the pathology develops, the symptoms of arthrosis become more noticeable: the knees begin to hurt at rest, and at night, during flexion and extension of the joint, extraneous sounds appear - crackles, crunches, clicks.Lameness, stiffness of movement and soft tissue swelling occur.
The following facts indicate the course of the disease:
- the appearance of deformation of the axis of the limbs in the form of O-shaped legs;
- constant pain, pain at night and when the weather changes (meteosensitivity);
- further deterioration of joint mobility with the development of flexion contracture;
- Weakness and atrophy of the thigh muscles.
Types and forms of the disease
There are:
- Primary.It develops as an independent disease.More often, such knee gonarthrosis is associated with age-related changes and heredity.
- Secondary.Occurs against the background of certain diseases or injuries, for example post-traumatic arthrosis.
Depending on the causes, the following types of arthrosis are distinguished:
- Ischemic, associated with problems with blood supply to tissues and vascular diseases;
- Post-infectious is caused by infections, viruses and autoimmune processes;
- The idiopathic nature of the development of the pathology remains unclear;
- Metabolism is associated with metabolic disorders – gout, hemochromatosis, chondrocalcinosis;
- Involutional as a result of age-related changes in the body;
- Post-traumatic, trauma history;
- Dishormonal – a result of hormonal imbalances in the body.
Stages of development
I. Osteoarthritis of the 1st degree - the initial stage is associated with a deterioration in the quality and quantity of synovial fluid (articular fluid, supplies the cartilage with nutrients, has shock-absorbing properties, promotes sliding of the articular surfaces).Malnutrition leads to wear and tear of the cartilage tissue and the appearance of the first signs of inflammation.In the early stages, movements are not affected.Patients experience mild pain, tingling and sometimes the joints may crack when moving.Symptoms occur during and after physical activity.Externally the knee looks quite healthy.
II. Arthrosis of the 2nd degree - leads to a thinning of the cartilage to 1.5-2.0 mm (normal 2.5-3.0 mm), there is a narrowing of the joint space and small individual bone growths (osteophytes) appear.The inflammatory process proceeds in waves and alternates between phases of remission and exacerbation.Gonarthrosis grade 1-2 is accompanied by swelling and weakness of the thigh muscles.The pain bothers me at rest, when the weather changes and I feel tired after walking.Movements become stiffer, morning stiffness and crunching in the joint appear.At this stage, patients most often consult a doctor.
III.Gonarthrosis of the 3rd degree is manifested by external deformation of the joint and curvature of the axis of the limb.The cartilage tissue is severely damaged, thinned to 1–1.5 mm, and exposed bone is visible in places.Bone growths are clearly noticeable under the skin and mobility is significantly restricted.With arthrosis of 2-3 degrees, the joint space narrows, the joints cannot bend and flex, all movements are accompanied by pain and crunching, and morning stiffness increases.A characteristic joint contracture develops.I'm afraid of stabbing pain in my knee, even when I'm resting.Patients often suffer from insomnia because they cannot assume a comfortable position that does not cause pain and because they feel changes in the weather.
IV. Grade 4 gonarthrosis is characterized by complete destruction of the articular surfaces, exposed bone is visible and the cartilage is represented by rare “islands”.The joint space is almost invisible.A pronounced O-shaped deformation of the lower extremities and swelling are noticeable.Mobility is almost completely lost.Treatment with non-surgical methods is ineffective at this stage;Joint replacement with an endoprosthesis is indicated.
An orthopedist says: In order to accurately determine the degree of arthrosis of the knee joint, in addition to examining the patient, an instrumental examination (ultrasound, X-ray or MRI of the joint) is extremely important.Since bilateral gonarthrosis is very common, it is recommended to examine both the left and right knee joints.This will help you choose the optimal treatment and prevent further progression of the disease.
diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, it is usually enough to perform an X-ray or ultrasound scan of the knee joint.In difficult cases, a laboratory examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are prescribed.If pathological fluid accumulates in the joint, a puncture and subsequent examination may be required.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Helps to detect the disease early.Allows you to measure the thickness of the cartilage layer, joint relief, the presence of synovial fluid, the size of osteophytes and ossifications.
Radiography
Conduct an assessment of the degree of damage and condition of bone and cartilage tissue.It shows the presence of osteophytes, narrowing of the joint space and joint deformation.In the early stages of the disease, the examination is not conclusive.
Analyzes
General blood and urine tests, as well as blood biochemistry, show signs of inflammation, the presence of infection and disorders in bone and cartilage tissue.They allow you to assess the general condition of the body, determine the causes of the disease and gonarthrosis, and exclude pathologies with similar symptoms.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging A highly precise diagnostic method that helps make the smallest changes visible.It helps in diagnosis both in early stages and in complex cases before surgical treatment.
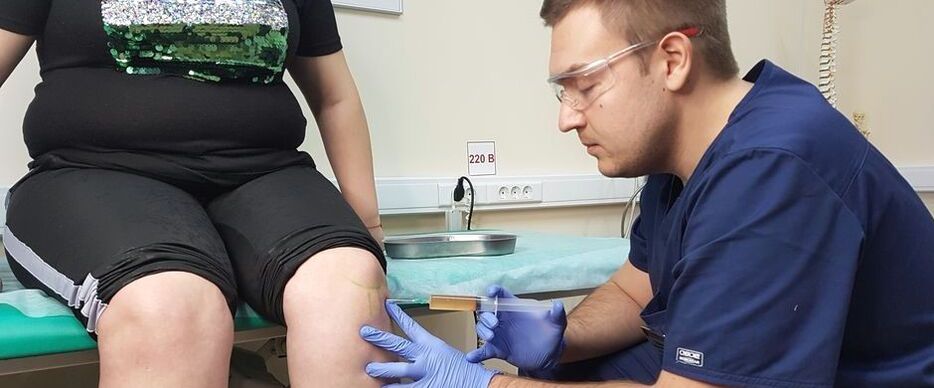
Which doctor is treating you?
The following specialists treat gonarthrosis of the knee:
- Orthopedic doctor – diagnoses the disease, intra-articular injections, plasma therapy, provides high-tech support and surgical treatment.
- Physiotherapist – responsible for instrumental physiotherapy treatment.
- Rheumatologist – helps if the disease is associated with autoimmune diseases.
- Sports doctor – required for a sports history.
- If the patient is overweight, a nutritionist is required.
During the recovery phase, the treating doctor can call in other specialists:
- Masseur – massages the lower extremities, restores muscle tone, thereby stimulating blood circulation and helping to restore joint mobility.
- Physiotherapist - selects special exercises and controls their implementation.
- Rehabilitation specialist – helps with the social adjustment of the patient;A specialist is particularly sought after after serious reconstructive operations on the knee.
What treatment is prescribed?
The earlier the disease is recognized and treatment of the symptoms of osteoarthritis begins, the greater the chances of recovery.Otherwise, the disease can lead to irreversible consequences and significantly worsen the quality of life.
Thus, treatment of 1-2 degrees of arthrosis of the knee joint has a good chance of completely restoring the function of the knee joint.Unfortunately, patients do not always seek medical help in the early stages.
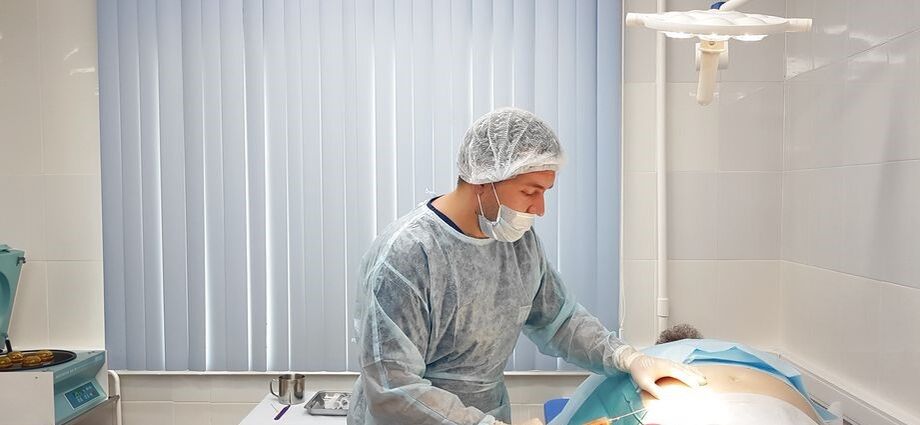

How can you relieve and treat pain quickly?
The first step is to eliminate pain and inflammation.Mandatory:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain relievers.The medication allows you to quickly eliminate inflammation in osteoarthritis and relieve pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroids are used when NSAIDs and analgesics do not help, for example in the treatment of grade 3 to 4 knee osteoarthritis.The patient is given a drug blockade - drugs are injected directly into the joint cavity.This helps reduce pain and provide relief within minutes of the injection.
- Special ointments and pain-relieving plasters.
An orthopedic doctor comments: The treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint of 2-3 degrees is always complex and usually includes more than 15 (!) recommendation points in the prescription form.It's not just medications and injections.This is a whole range of rehabilitation measures aimed at correcting the biomechanics of the joint and the patient's lifestyle.Only this approach will help preserve the joint and stop the progression of the disease.
Preparations that strengthen bone and cartilage tissue:
- Chondroprotectors based on chondroitin and glucosamine are the nutritional basis of the chondrocytes.
- Hyaluronic acid preparations serve as analogues of synovial fluid.
- Drugs that improve microcirculation and blood supply to the articular cartilage.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements strengthen the bones that form the knee joint.
- Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid preparations, an artificial analogue of synovial fluid, help lubricate the articular surfaces.
- Medicated blockades help to quickly relieve swelling, pain and inflammation.The effect is usually noticeable the next day.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint also includes physiotherapy:
- Electrophoresis.The medicine penetrates the affected area using an electric current.Electrophoresis is used to treat knee pain due to gonarthrosis.
- Phonophoresis.The medicine enters the area of inflammation under the influence of sound waves.An additional advantage of the method in the treatment of deforming gonarthrosis is the thermal effect.
- Shock wave therapy.The procedure improves blood circulation, stimulates tissue nutrition and serves to destroy osteophytes and scar tissue.
- Traction therapy (joint traction) – helps to relieve the joint space, stretching it by several millimeters and thereby reducing the mutual pressure of the joint surfaces.
- Electromyostimulation – stimulates blood circulation and muscle function using electrical current and restores muscle tone.
- Using special robotic simulators, mechanotherapy helps develop movements in the joint and combat contractures.
- Laser therapy creates deep tissue heating and reduces the inflammatory response.
- Magnetic field therapy.The therapeutic effect is based on the properties of the magnetic field to reduce pain, inflammation and tissue swelling.
Orthobiological methods are aimed at stimulating regeneration and replacing defects in cartilage tissue:
- Plasmolifting is a plasma-based drug that is made from the patient's own blood, triggers regeneration processes and contains growth factors.
- PRP therapy – plasma obtained from the patient's blood is used as medicine.Platelet-rich plasma stimulates the regeneration of chondrocytes and alleviates the inflammatory process.
- SVF therapy is based on the use of stromal vascular fraction cells obtained from the patient's own adipose tissue.
- SVF therapy + PRP therapy – by using concentrated plasma and progenitor cells at the same time you achieve the best results.
- Stem cell treatment.The method is based on the use of bone marrow cells and is currently under development.
Each case is individual and requires the development of a separate rehabilitation program for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint.
Don't know where to treat osteoarthritis?Would you like to seek professional help and undergo treatment without surgery?Sign up for a health center.We offer you to undergo an examination and start restoring your health on the day you contact us.Benefit from modern knee osteoarthritis treatment at competitive prices.




















